How to build Micro-Frontend Architecture with Web Components and BFF (part 1/2)?

This is blog post handles Micro-Fronted Architecture and how to utilize Web Components via Backed for Frontend.
What is Micro-Frontend Architecture?
Micro-frontend architecture is a design approach in which a front-end app is decomposed into individual, semi-independent “microapps” working loosely together. The micro-frontend concept is vaguely inspired by, and named after, microservices. - Bob Myers (Building a Micro-frontend Framework | Toptal)
Teams are usually responsible for their own specific domain area like products, invoices, orders, customer data, etc. in large enterprises. Each team has the best knowledge about their own domain and they have full ownership of that domain. Traditionally in Microservice architecture team owns API endpoints and a Database that contains domain-specific data. The micro-frontend architecture enables the domain team can also deliver domain-specific User interfaces "microapps" for the consumers. Typically in a web environment these "microapps" are delivered as a Web Component.
Basically Web Component is a generic Javascript/HTML-based component/library that is embedded in the consumer application. The web Component producer team has full ownership and control of all functionalities inside the Web Component.
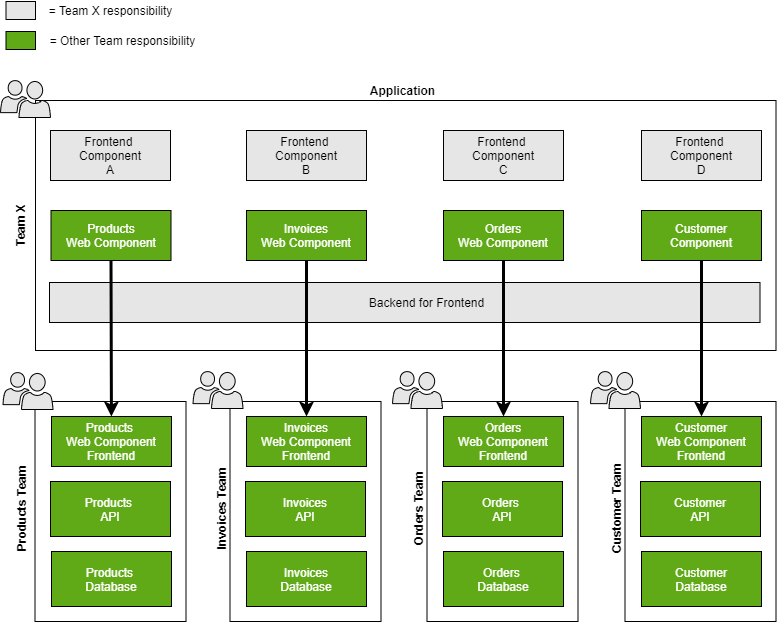
Web Component-consuming options
I introduce here two options on how to consume Web Component delivered by other teams.
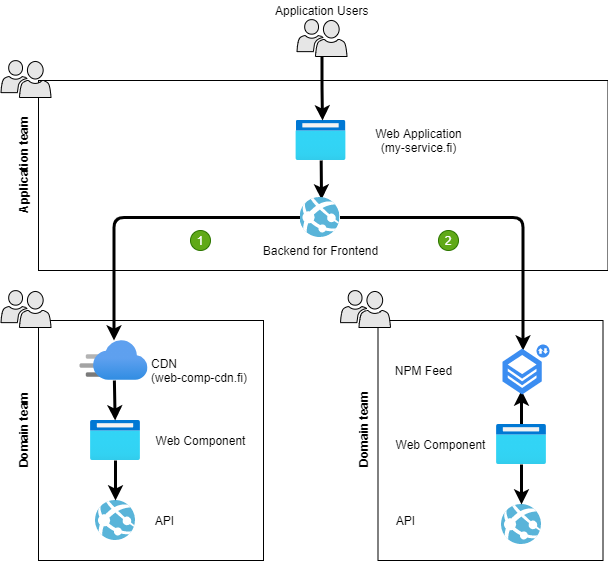
1. Consuming Web Components directly from the producer
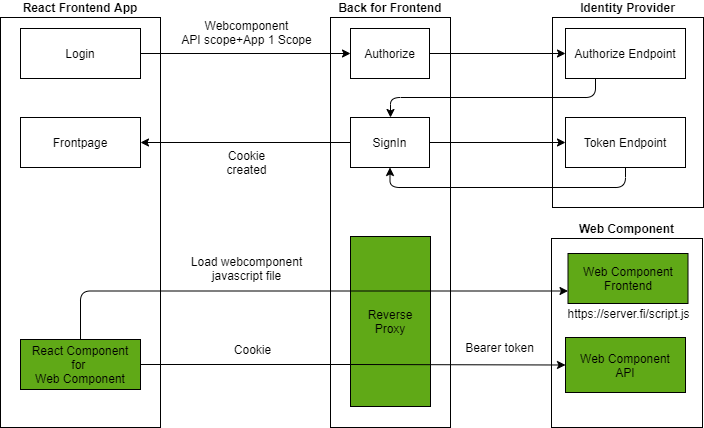
In this case, the Web Component javascript file is fetched from another server via Backed for Frontend proxy. BFF enables that Web Component javascript file to be treated as same-origin and then the same-site cookie will work. API requests with same-site cookies from the Web Component User interface will be re-routed via BFF. BFF extracts the bearer token from the cookie and passes it further to the destination API. Note! Authorization Scope of Web Component API is needed to request during the Authorization flow.
2. Consuming Web Component via ex. NPM
Web Component (javascript) is bundled into the NPM package which is added to the consumer application. In this scenario Web Component's javascript/html files are part of the consumer application so there are no problems with same-site cookies. API requests will be re-routed via BFF also in this scenario.
Summary
What are the pros & cons of Micro-Frontend Architecture?
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
The next blog post shows code samples of how to consume Web Components directly from the producer via BFF.
Comments